Housing productivity has emerged as a critical issue in the discourse around the American housing crisis, significantly impacted by land-use regulations and NIMBY policies. Despite the impressive growth in productivity across various sectors, the construction industry has faced stagnation, exacerbating the challenges of housing affordability. The interplay between tighter regulations and a lack of innovation in building practices has led to an alarming increase in the cost of new homes, which has more than doubled since 1960. These constraints not only limit the scale of developments but also distort market dynamics, pushing homeownership further out of reach for many Americans. As we explore the vital connection between housing productivity and these external factors, it becomes clear that addressing this disparity is essential for fostering a more sustainable and accessible housing market.
The efficiency of housing production plays a pivotal role in determining the overall accessibility and affordability of homes. It encompasses the effective use of resources in construction, influenced heavily by local legislative constraints related to land usage and community opposition to new developments. As economic challenges mount within the housing sector, alternative terms like construction efficiency and residential output serve to emphasize the underlying issues at play. Facilitating discussions around the intricacies of housing deployment, including the restrictions imposed by zoning laws and the ongoing impacts of community policies, is crucial for understanding the broader landscape of home availability. By delving into these interconnected aspects, we can better grasp the realities of the current housing situation and the steps necessary for improvement.
Understanding Housing Productivity Challenges
Housing productivity in the United States has faced significant challenges, particularly due to an array of land-use regulations that are often influenced by NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies. These regulations have fostered an environment where large-scale housing developments are increasingly difficult to initiate, thereby reducing the overall efficiency and output of construction firms. A decline in housing productivity is evident when comparing current building practices to those from past decades, where large projects dominated the market. This shift has not only impacted the scale of development but has also stifled innovation within the industry.
The substantial reduction in productivity—from the heights of the post-war era to today—can be attributed to the intricate web of local zoning laws that complicate the ability to manage larger construction projects effectively. Historically, homebuilders benefitted from economies of scale, allowing them to mass-produce affordable homes. Presently, the fragmentation of projects means that smaller firms dominate the landscape, leading to inefficiencies and higher costs for consumers. Addressing these issues is critical not only for housing affordability but also for restoring productivity in the construction sector.
The Impact of NIMBY Policies on Housing Availability
NIMBY policies have significantly contributed to the current housing crisis by restricting development in communities. These policies often arise from residents’ concerns about maintaining neighborhood character, property values, or potential increases in traffic. In pursuit of these local interests, neighborhoods implement stringent land-use regulations that can create barriers for builders, ultimately limiting the supply of new homes. As the aforementioned research indicates, this persistent opposition to development has led to a marked decrease in large-scale housing projects, exacerbating the affordability crisis for many Americans.
The consequences of NIMBYism extend beyond immediate localities; they resonate throughout the housing market as a whole. With fewer new homes entering the market, demand surges, driving prices even higher. This phenomenon disproportionately affects low- and middle-income individuals, who find themselves increasingly priced out of homeownership. The trend suggests that unless a cultural shift occurs around the acceptance of housing developments, particularly affordable and diverse types of housing, the cycle of unaddressed need and rising costs will persist.
Examining Land-Use Regulations and Their Consequences
Land-use regulations exist with the intention to organize community growth and protect the character of neighborhoods, but they often have unintended consequences that stifle housing productivity. The historical analysis shows that as these regulations have intensified since the 1970s, the productivity in housing construction has sharply declined. Builders now face multiple barriers, including excessive zoning requirements and lengthy approval processes that can delay or derail potential projects altogether.
These regulations disproportionately benefit existing homeowners who may resist new developments due to fears of diminishing property values or unwanted local changes. However, this situation creates a dilemma: the need for new housing remains critical to address the growing population and the demand for affordable living spaces. Balancing the interests of current residents with the pressing need for new housing is essential for creating a productive and sustainable building environment.
The Role of Innovation in Construction Productivity
Innovation is a crucial factor in increasing productivity within the construction sector, yet recent trends indicate a significant stagnation in this area. Historically, builders were at the forefront of innovation, introducing new techniques and materials that improved efficiency and reduced costs. However, since the 1970s, patenting activity in construction has decreased sharply, suggesting that the industry has fallen behind others, such as manufacturing, where innovation continues to thrive.
The decline in innovation can largely be attributed to the smaller size of firms that dominate the construction market today, many of which lack the resources and incentive to invest in research and development. Without a focus on innovative building techniques and materials, the industry struggles to overcome the challenges posed by rising costs and productivity barriers. Encouraging larger firms and new entrants to innovate in the housing sector could play a pivotal role in revitalizing housing productivity and improving affordability for future generations.
Housing Affordability: A Nationwide Concern
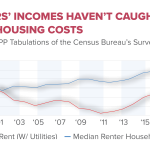
The issue of housing affordability has escalated into a nationwide crisis, restricting homeownership potential for millions of Americans—especially the younger generations. The stark increase in housing prices compared to stagnant wages has widened the gap between the aspiration of owning a home and the reality for many. As highlighted in the research, the average cost of a new single-family home has doubled since 1960, indicating a systemic dilemma that must be addressed at various levels of governance.
With the construction industry’s productivity in decline and facing substantial regulatory hurdles, the prospect of affordable housing remains dim. Innovative policy solutions are necessary to reform land-use regulations and embrace new building practices that can enhance productivity while ensuring that homes remain accessible to those in need. Only by recognizing and addressing these intertwined challenges can the country hope to enhance housing affordability and provide solutions for future generations.
The Intergenerational Transfer of Housing Wealth
A concerning trend has emerged regarding the intergenerational transfer of housing wealth, where younger demographics find themselves significantly disadvantaged compared to their older counterparts. This expenditure shift, where assets are increasingly concentrated among older homeowners, prevents younger generations from accruing similar wealth through property ownership. As reported, median housing equity for younger earners has plummeted, contrasting sharply with the stable financial gains of older generations, which raises critical questions about economic equity and opportunity.
The disparity in housing wealth can primarily be linked to the current housing crisis and the systemic barriers that prevent new entrants from accessing the market. If the current trends continue, the gap in wealth accumulation will likely widen, affecting not only individual family stability but also the broader economy. Addressing the fundamental issues within housing supply and related policies is essential to ensure that future generations have the opportunity to build their wealth through homeownership.
Historical Perspectives on Housing Development
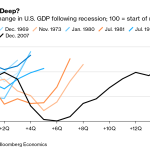
Examining the history of housing development in the U.S. reveals extensive shifts that have occurred over the decades, reflecting both societal values and economic conditions. D’Amico’s research illustrates that the post-war boom saw large-scale developments become the norm, driven by innovations in construction and mass production techniques. However, since 1970, there has been a significant shift towards smaller, individualized projects. This change mirrors societal attitudes towards land-use and development, as local communities became more protective about their residential environments.
This historical perspective highlights a pressing need for revitalization in the approach to housing development, allowing for larger, more efficient projects that can meet the growing demand. Learning from past successes in large-scale housing production could offer valuable insights into future strategies aimed at increasing efficiency and driving down costs. Ultimately, reviving this model could play a pivotal role in addressing today’s housing affordability crisis.
Fostering Collaborative Solutions for Sustainable Development
In light of the pressing housing crisis, collaborative solutions are urgently needed among various stakeholders, including policymakers, builders, and community members. Fostering dialogue and cooperation can help bridge the gap between local interests and the broader need for housing development. By engaging communities in the planning process, there is potential to address concerns while also promoting innovative and sustainable building practices that can lead to increased productivity in the construction sector.
Successful collaboration could pave the way for more flexible land-use regulations that facilitate profitable large-scale projects without sacrificing community integrity. As cities grapple with population growth and infrastructural challenges, re-thinking traditional models of housing development will be crucial in creating institutions that prioritize both comprehensive planning and inclusivity. Through proactive collaboration, communities can better position themselves to tackle housing affordability head-on while also enhancing the overall quality of life for their residents.
The Promise of Modern Construction Techniques
Modern construction techniques hold great promise for revitalizing housing productivity and tackling the affordability crisis. Innovations such as modular and prefabricated housing have arisen as potential solutions to streamline the construction process, reduce costs, and improve efficiency. By leveraging technology effectively, builders can create homes faster and more sustainably, addressing the pressing demand for affordable housing.
Implementing these modern techniques at a larger scale can mitigate some of the longstanding issues associated with traditional construction methods, particularly those exacerbated by stringent land-use regulations. By overcoming these barriers and encouraging the adoption of innovative construction practices, the industry can set a new standard for housing development that prioritizes affordability, accessibility, and sustainability for a growing population.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do land-use regulations impact housing productivity?
Land-use regulations significantly constrain housing productivity by limiting the scale and nature of construction projects. This micromanagement forces builders to craft unique homes tailored to various local demands, instead of leveraging mass-production techniques that could lower costs and enhance efficiency.
What role do NIMBY policies play in the housing crisis?
NIMBY policies contribute to the housing crisis by resisting new developments in local communities. These policies create obstacles for builders, reducing the availability of affordable housing and perpetuating the cycle of rising home prices, ultimately limiting housing options for many potential buyers.
Why is construction productivity declining in the housing sector?
The decline in construction productivity within the housing sector can be attributed to increased land-use regulations and smaller project sizes. As builders face more restrictions, their ability to innovate and adopt efficient building practices diminishes, leading to lower output and higher costs.
How are housing affordability and construction productivity connected?
Housing affordability is closely tied to construction productivity; as productivity declines due to regulatory constraints, the cost of building homes rises. This results in fewer affordable housing options, exacerbating the housing affordability crisis that many regions are currently facing.
What measures can enhance construction productivity in housing?
Enhancing construction productivity in housing may involve revising land-use regulations to allow larger, more standardized developments. Encouraging mass production techniques and reducing bureaucratic hurdles can enable builders to innovate, increase efficiency, and ultimately lower housing costs.
What is the relationship between NIMBYism and housing affordability?
NIMBYism directly impacts housing affordability by hindering the construction of new homes. By preventing developments that increase housing supply, NIMBY policies drive up costs, making it increasingly difficult for residents to find affordable housing.
How have historical trends affected housing productivity over time?
Historically, U.S. housing productivity soared from 1935 to 1970, significantly outpacing other industries. However, after 1970, as local land-use regulations increased, construction productivity fell dramatically, leading to higher costs and exacerbating the housing crisis.
What is the significance of large housing projects for construction productivity?
Larger housing projects are vital for improving construction productivity as they allow builders to take advantage of economies of scale. These projects can produce more housing units per worker, thereby increasing overall productivity and helping to stabilize or reduce housing costs.
How does the construction industry’s innovation compare to other industries?
The construction industry has lagged in innovation since the 1970s, particularly in comparison to manufacturing. While manufacturing has seen a rise in patents and innovative practices, construction has struggled, partially due to the constraints imposed by land-use regulations and smaller project scales.
What are the implications of lower construction productivity for future housing markets?
Lower construction productivity has severe implications for future housing markets, leading to fewer new homes being built, higher prices, and exacerbated housing shortages. If productivity does not improve, the housing affordability crisis is likely to worsen, affecting many American families.
| Key Points |
|---|
| U.S. housing construction productivity has declined significantly since the 1970s, primarily due to stricter land-use regulations and NIMBY policies. |
| The cost of new single-family homes has more than doubled since 1960, largely due to increased labor and material costs as well as regulatory barriers. |
| Construction firms today are much smaller compared to the post-WWII era, leading to decreased efficiency and innovation. |
| Large builders can produce four times more housing units per employee than smaller firms, highlighting the importance of economies of scale in housing productivity. |
| Productivity in manufacturing has continued to rise, contrasting sharply with the stagnation in the construction sector since the introduction of more land-use regulations. |
| The decline in housing productivity contributes to rising housing prices, affecting affordability and accessibility for many Americans. |
Summary
Housing productivity has become a pressing issue in the U.S., as tighter land-use regulations and NIMBY policies have stifled efficiency and innovation within the construction sector. With rising costs of homeownership, it’s clear that addressing these regulatory barriers is crucial for revitalizing housing productivity and ensuring affordable options for future generations.