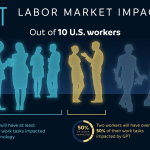
AI labor market disruption is becoming increasingly evident as we witness a seismic shift in employment dynamics across various sectors. This phenomenon is driven by rapid advancements in AI technology, which are reshaping labor market trends and altering the landscape of job availability. As businesses integrate automation into the workforce, we encounter significant occupational churn, particularly affecting middle-skill jobs. This trend raises questions about the sustainability of traditional employment and points towards a new era of STEM job growth, where skill-intensive roles are becoming more prominent. By analyzing these changes, we uncover insights into the future of work and the implications of automation on a broad scale.
The transformative influence of artificial intelligence on job markets is leading to an unprecedented disruption in how work is organized and performed. As automation permeates various industries, we are witnessing a shift in job opportunities that is reminiscent of historical technological revolutions. With the rise of advanced technologies, professionals are increasingly experiencing occupational volatility, prompting discussions about workforce adaptation. Additionally, the burgeoning demand for roles in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) indicates a clear trend towards skill-specialized employment. Understanding these developments is crucial for navigating the evolving landscape of the modern economy.
The Impact of AI on Labor Market Trends
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is now being recognized as a significant force reshaping labor market trends. According to recent research co-authored by Harvard economists, AI technology is not just a fleeting trend; it’s influencing sectors in ways that mirror historical technological shifts, such as the introduction of electricity and mass production. Labor analysts are observing a clear pivot towards high-skilled and high-paying jobs as AI tools become more integrated into the workforce. This change reflects a growing need for advanced training in fields like data analysis and software development, which are burgeoning in response to technological advancements.
As AI continues to evolve, we see a corresponding shift in labor dynamics, particularly within the STEM sectors. The study highlights a 50% increase in the share of STEM jobs from 2010 to 2024, indicating a rapidly growing demand for skilled professionals. Firms are not only looking for technical talent but are also investing significantly in new technologies, reaffirming the notion that jobs requiring technological know-how will dominate the landscape, shaping employment opportunities in the years to come.
Understanding Occupational Churn in the Age of AI
Occupational churn, or the turnover rate within professions, has been a defining factor in understanding the labor market’s evolution over the last century. The historical analysis undertaken by the Harvard researchers reveals contrastive periods of stability and volatility. Particularly, the recent surge in AI technology has reignited concerns about job displacement. While the decades prior to 2019 showed low rates of churn, the advent of AI has stimulated discussions about the future of various occupations—especially those considered low-skilled.
AI’s disruptive potential is evident as certain job categories have seen significant declines due to automation and AI integration. Conversely, industries that are embracing technology have adapted, showcasing resilience and growth. The findings draw attention to the necessity for workers to adapt to these changes, emphasizing the importance of lifelong learning and upskilling in an increasingly automated workforce. As the paper suggests, adapting to AI will not only be advantageous but essential for long-term career viability.
Automation and Its Role in Workforce Evolution
Automation, closely tied to the rise of AI technologies, continues to transform the workforce landscape. The Harvard study indicates that many low-wage service sectors might not recover post-pandemic due to the competition from automated processes. This trend of automation has resulted in fewer positions available for roles that previously were abundant, necessitating a pivot in employment strategies and educational focus towards more skilled occupations.
Moreover, the paper points out that while automation has caused tremors in job security for many, it has started creating new opportunities, particularly within high-tech industries. Jobs in data science, algorithm development, and AI management are on the rise, urging existing workers to consider reskilling their profiles. The dual effect of automation indicates the complexities of AI’s impact—while it displaces some jobs, it is also fostering the demand for others, leading to an evolution rather than a mere decline of jobs.
The Rise of AI-Driven STEM Job Growth
In the evolving job market, there is a pronounced emphasis on STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) roles. The researchers highlight a significant uptick in STEM job growth in recent years, with positions such as software developers and data analysts commanding increasing attention and investment. This growth reflects broader labor market trends inclined towards careers that leverage AI capabilities, thus reshaping educational pathways and employment structures.
The increase in STEM jobs is not just a numerical rise; it signifies a behavioral shift in how industries seek to harness technological advancements. Companies are recognizing that innovation stems largely from the expertise of skilled workers in these fields. The data supports the assertion that job seekers with STEM skills are not only more likely to find employment but also to command higher salaries, designating STEM fields as critical components of future workforce strategy.
Navigating Job Polarization in the Age of AI
Job polarization—where middle-income job opportunities diminish while both low and high-paying jobs proliferate—is becoming increasingly apparent with the rise of AI technologies. The research identifies a unique trend where higher-wage jobs are seeing growth, while middle-income roles are stagnating. This trend is concerning as it draws a dividing line in the job market, favoring highly skilled individuals, while leaving a gap for those without advanced degrees or training.
The consequences of job polarization highlight the need for educational institutions and policymakers to address this growing divide. As AI continues to influence labor dynamics, equipping the workforce with the necessary skills to thrive in high-paying roles will be crucial. This could entail a restructuring of educational programs toward technical training and skill advancement, crucial in mitigating the adverse effects of job polarization in an AI-centric economy.
AI Labor Market Disruption and Future Predictions
The disruption brought about by AI is not merely a current trend but is anticipated to have lasting implications for the labor market. As technology continues to evolve, labor economists predict more profound shifts in job availability, skills needed, and employment structures. The data from the Harvard study reveals that the onset of AI has started new cycles of occupational churn, reflecting the constant adaptation required to keep pace with technological advancements.
What is striking about these predictions is the assertion that even knowledge-based roles will experience a transformation due to AI. Organizations may begin to leverage advanced AI capabilities for routine tasks, demanding more from employees who must adapt quickly to these changes. This evolution will likely lead to a workforce that is not only more tech-savvy but also better prepared to navigate an environment where AI plays an integral role.
The Disappearing Low-Wage Jobs: A New Reality
The transformation of the labor market by AI is leading to substantial decline within low-wage job sectors. The findings from the Harvard research indicate that positions which experienced growth in prior decades, particularly within the service industry, are now subject to significant contraction. The decline in these jobs raises concerns about long-term employment trends, as many of these positions might not return even as the economy rebounds.
Moreover, the shift towards online services and automation in these sectors points towards a more permanent alteration in how employers operate. Companies are finding efficiencies in automation, which poses the question of whether low-wage jobs will continue to exist at pre-automation levels. This trend calls for urgent discussions around labor policies, living wages, and support systems to aid workers transitioning out of declining industries.
The Future of E-Commerce and Retail Sales Jobs
E-commerce represents a sector that has exponentially grown, further fueled by the integration of AI technologies. The decline in retail sales jobs amid the rise of online shopping platforms illustrates how consumer behavior is changing in response to technological disruptions. The paper indicates a 25% decrease in retail sales jobs as businesses adopt predictive AI technology, which streamlines operational processes and enhances customer engagement.
This shift suggests that future retail jobs may require new skill sets focused on digital marketing, data analytics, and technology management. As customers increasingly prefer online shopping experiences, it is paramount for job seekers to align their skills with industry demands. Retailers’ ability to adapt to these changes will determine their survival, and understanding AI’s role in these transformations will be crucial for future workforce planning.
Preparing Knowledge Workers for an AI-Driven Future
AI’s emergence into the labor market necessitates a reevaluation of roles traditionally considered secure, particularly for knowledge workers in sectors like finance and journalism. The study indicates that while automation may displace some roles, it will also foster an environment where productivity expectations increase, pushing knowledge workers to adapt to demands for quicker outputs and performance.
This expectation for rapid results underscores the importance of investing in education and continuous learning. Knowledge workers must not only be familiar with the technologies they use but also demonstrate flexibility in integrating these tools into their workflows effectively. Employers are likely to seek individuals who can leverage AI technologies to enhance productivity without compromising quality, making adaptability a critical skill moving forward.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI labor market disruption impacting job security in various sectors?
AI labor market disruption is significantly altering job security across various sectors. While certain low-wage jobs are declining, the demand for STEM positions is increasing, indicating a shift towards higher-skilled occupations. This trend poses potential risks for workers in sectors susceptible to automation, emphasizing the need for reskilling and upskilling to remain competitive.
What trends are emerging in the labor market due to AI technology impact?
Recent trends driven by AI technology impact include a decrease in job polarization, with a notable increase in high-paid job opportunities in STEM fields. Additionally, the decline of low-wage service jobs and retail sales positions is evident, highlighting the transformative effect of automation in the workforce.
Why is understanding AI labor market disruption essential for today’s workforce?
Understanding AI labor market disruption is essential as it not only influences job availability but also shapes the skills required in the modern economy. Knowledge workers, in particular, must adapt to technological advancements to maintain relevance in their fields, making awareness of these changes critical for career sustainability.
What role do STEM job growth and AI play in the changing labor market?
STEM job growth plays a crucial role in the changing labor market, fueled by AI advancements. As demand for technical expertise rises, organizations are increasingly investing in AI-related roles, leading to a surge in job opportunities within science, technology, engineering, and mathematics fields. This shift underscores the importance of STEM education in adapting to future labor market trends.
How does occupational churn relate to AI labor market disruption?
Occupational churn, which reflects the volatility within job sectors, is closely linked to AI labor market disruption. Historical data indicates that periods of high churn correlate with technological advancements, including the current phase marked by AI. The dynamic nature of occupational shifts necessitates ongoing adaptation from the workforce to align with evolving job demands.
What are some long-term risks associated with AI labor market disruption for workers?
Long-term risks associated with AI labor market disruption for workers include job displacement in roles vulnerable to automation and increased expectations for productivity. As companies leverage AI to enhance efficiency, knowledge workers may face pressure to deliver results more rapidly, potentially leading to job insecurity if they cannot keep pace with technological advancements.
| Trend | Description | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| End of Job Polarization | Shift from a barbell pattern in job distribution to a predominance of high-paid jobs for skilled workers. | Increased demand for advanced skills and education. |
| Rise of STEM Jobs | Significant growth in STEM job sectors from 6.5% to nearly 10% in share from 2010 to 2024. | Greater emphasis on hiring technical talent and investments in technology. |
| Decline in Low-Wage Jobs | Flat or declining employment in low-wage service sectors since 2019. | Potential longer-term displacement of low-wage workers. |
| Reduction of Retail Sales Jobs | Decrease from 7.5% to 5.7% in retail employment from 2013 to 2023, accelerated by e-commerce and AI. | Shift towards online shopping habits and reduced demand for traditional retail roles. |
Summary
AI labor market disruption is becoming increasingly evident as technologies evolve and reshape the job landscape. The recent study by Harvard economists reveals significant shifts in occupational trends over the past century, particularly noting a concerning decline in low-wage jobs alongside a surge in high-skilled positions. As AI continues to integrate into various sectors, organizations are likely to prioritize technical skills and training, ultimately transforming workforce dynamics. This ongoing change underscores the need for workers across all professions to adapt to the advancing landscape driven by AI, ensuring they remain relevant and competitive in a rapidly evolving job market.