The recent Federal Reserve rate cut is expected to have significant implications for consumers and the broader economy. As the Fed lowers interest rates, we can anticipate more favorable mortgage rates, making home buying increasingly accessible. Economists, like Jason Furman, emphasize that this rate cut can stimulate economic growth by easing the cost of borrowing for businesses and consumers alike. Moreover, as inflation continues to be a concern, this strategic move by the Fed reflects a careful calibration of its policy to promote stability in the financial markets. Overall, the impact of this decision could resonate across Wall Street and Main Street, offering hope for those managing credit card debt and hoping to secure lower loan rates for larger purchases.
In a pivotal move for the economy, the recent decision by the central bank to reduce borrowing costs marks a critical shift in monetary policy. This rate adjusting maneuver opens the door for decreased interest rates across various sectors, potentially lowering the financial burden for consumers seeking mortgages or loans. Many analysts argue that easing monetary conditions is essential for stimulating growth, particularly amid concerns about rising inflation and its effects on spending power. The implications of such a strategy are substantial for both individual households and businesses, paving the way for easier access to financing. As we navigate this evolving economic landscape, understanding the nuances behind this decision and its ripple effects will be crucial for anticipating future market dynamics.
Impact of the Federal Reserve Rate Cut on Borrowing Costs
The recent decision by the Federal Reserve to cut interest rates by half a percentage point is a significant step aimed at reducing borrowing costs for consumers. This rate cut is expected to benefit various sectors, especially those relying on credit, including credit card users and potential homebuyers. Lower interest rates typically encourage spending and investment, allowing consumers to borrow more affordably. As the Fed eases its monetary policy, the effects are likely to ripple through the economy, stimulating growth in industries that heavily depend on loans.
Moreover, as mortgage rates begin to decrease in response to the Fed’s aggressive rate cut, homebuyers may find it easier to afford homes in a market that has recently been under strain from high borrowing costs. This dynamic could unlock stalled real estate transactions, contributing to a boost in economic activity. While some may argue that such a cut could stoke inflation, the Fed appears committed to closely monitoring economic indicators to ensure that the balance between growth and price stability is maintained.
Expectations for Future Interest Rate Cuts
Given the strong indications from Fed Chairman Jerome Powell regarding potential further rate cuts, economists anticipate that the Federal Reserve may implement two additional cuts by the year’s end. This foresight helps market participants adjust their strategies and decisions accordingly, as lower rates typically correlate with enhanced economic conditions, including job growth and consumer confidence. However, it’s crucial to acknowledge the Fed’s careful stance on this matter.
The Fed aims to remain flexible, ready to pause or alter its course based on emerging data, particularly if inflationary pressures resurface. This approach reflects the dual mandate of the Fed: to promote maximum employment while ensuring price stability. The potential of receiving two more cuts indicates a proactive method in managing economic conditions without prematurely compromising the progress already made towards a healthy labor market.
The Relationship Between Fed Policy and Inflation
As the Federal Reserve continues to adjust interest rates, a key focus remains on managing inflation levels. The Fed’s latest rate cut comes amid a mixed bag of inflationary signals, and it aims to create an environment conducive to sustained economic growth. Lower interest rates generally help stimulate demand in the economy, which may lead to rising consumer prices if supply does not keep pace with demand. However, the Fed’s continuous monitoring of inflation trends suggests vigilance in ensuring that price increases do not spiral out of control.
Economists predict that while the initial impact of the rate cut may lead to higher inflation temporarily, a well-paced approach in easing policy will be essential in achieving a balance. By signaling readiness to intervene further if necessary, the Fed can help manage expectations and encourage businesses and consumers to spend, invest, and grow the economy. Thus, maintaining inflation in check, while navigating lower borrowing costs will require comprehensive monitoring of economic indicators.
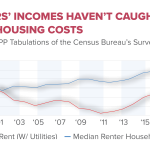
Mortgage Rates and Housing Affordability Post-Rate Cut
Following the Federal Reserve’s decision to cut rates, experts believe that mortgage interest rates are likely to decrease further, providing much-needed relief for prospective homebuyers. As mortgage rates decline, the implications for housing affordability become significant, particularly in an environment where prices have outpaced wage growth. This decrease can potentially reinvigorate the housing market as more buyers may find homes within their budget.
However, while declining mortgage rates are a positive sign, it remains important to consider that current rates are still relatively high compared to historical averages. As the Fed continues to implement its easing policy, the ultimate goal will be to create not just favorable financing conditions but also a broader impact on housing supply and affordability. Addressing the nationwide housing crisis involves multiple factors, including supply chain issues and regulatory hurdles, which may take time to resolve as the market adjusts.
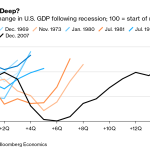
Long-Term Economic Effects of Rate Cuts
While the immediate effects of the Federal Reserve’s rate cuts are likely to manifest in reduced borrowing costs, the long-term consequences for the economy are still uncertain. As businesses adjust to more favorable financing conditions, there could be a gradual uptick in investment and job creation. An environment with lower interest rates typically encourages companies to take on new projects and expand operations, ultimately contributing to economic growth.
Nonetheless, the potential for increased inflationary pressure remains a concern. If economic growth accelerates too rapidly, it might lead to tighter labor markets, prompting wages to rise and consequently increasing inflation. The Fed’s challenge lies in ensuring that the economy does not overheat while fostering an environment conducive to expansion. Keeping a careful eye on economic indicators will be essential for the Fed in determining the timing and extent of any future monetary policy adjustments.
Consumer Debt and Payment Relief Expectations
As consumers eagerly await the benefits of the recent Fed rate cut, there remains uncertainty regarding how soon they will experience relief on their debts. Lower interest rates are expected to eventually translate into lower payments on credit cards and other loans. However, due to factors such as repayment risk and market expectations, it may take time for these reductions to materialize effectively across all consumer credit markets.
For many borrowers, particularly those struggling with high-interest debt, the anticipation surrounding future rate cuts could influence spending habits and consumer confidence. Yet, it is important to note that while interest rates are poised to decline, achieving significant reductions in consumer debt levels will require disciplined financial strategies and a more favorable economic environment. As consumers navigate these changes, being proactive in debt management and financial planning will be crucial to optimizing their economic circumstances.
The Signal of Market Reactions to Fed Cuts
The market’s reaction to the Fed’s interest rate decisions often provides valuable insights into consumer confidence and economic expectations. Following the announcement of the rate cut, stock market investors typically perceive this move as a signal of a supportive economic climate that can foster growth. This optimism often leads to a surge in stock prices, reflecting a collective belief that lower borrowing costs can spur corporate earnings and economic activity.
Furthermore, the interconnectedness of various financial markets means that movements in interest rates can generate pronounced effects on investment patterns. As bond yields decline following a rate cut, it can prompt a shift of capital towards equities, enhancing investment in the stock market. For business owners and investors alike, understanding these market shifts becomes essential for making informed decisions in an evolving economic landscape.
Navigating Economic Uncertainty Amid Fed Policies
In the backdrop of fluctuating economic indicators, the Federal Reserve’s policy changes introduce a layer of uncertainty that businesses and consumers must navigate. The recent rate cut, while temporarily beneficial, necessitates vigilance as further developments unfold. Businesses must remain adaptable amid changing economic conditions, seeking ways to optimize operations and capitalize on the favorable financing environment created by the Fed’s actions.
Consumers, on the other hand, are encouraged to adopt a proactive approach in managing their financial decisions, especially as they wait for the impact of the rate cut on their debts. The uncertainty surrounding future rate adjustments may lead families to reevaluate their spending, saving, and investment strategies to ensure greater financial stability. The adaptability of consumers and businesses alike will significantly shape the overall economic landscape in response to the Fed’s policies.
Federal Reserve’s Dual Mandate: Employment and Inflation
The Federal Reserve operates under a dual mandate to foster maximum employment while ensuring price stability. This balancing act is crucial, especially when considering the implications of recent rate cuts on these two fronts. While facilitating lower borrowing costs is designed to stimulate job creation, the Fed must simultaneously be mindful of potential inflationary pressures that can arise from increased economic activity.
This dual challenge has led the Fed to adopt a cautious approach, implementing rate cuts while closely monitoring labor market developments. Should signs of overheating emerge, the Fed may need to take corrective action to maintain inflation within its targeting range. Thus, effectively managing this delicate balance is key to nurturing sustainable economic growth while safeguarding against erratic price fluctuations.
Guidance for Consumers Post-Interest Rate Cuts
Consumers are often left wondering how best to navigate their finances after the Federal Reserve announces interest rate cuts. While lower rates can signal a more favorable borrowing environment, they also come with implications for savings and investment strategies. One approach consumers might consider is refinancing existing loans, particularly mortgages, to take advantage of lower rates, which can reduce monthly payments and overall interest costs.
Additionally, consumers should engage in careful budgeting and expenditure planning, especially amidst uncertainties regarding future economic conditions. With the possibility of further rate cuts, understanding how these changes affect personal finance decisions can empower consumers to capitalize on upcoming opportunities while safeguarding their financial well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the Federal Reserve rate cut impact mortgage rates?
The Federal Reserve rate cut typically leads to lower mortgage rates. As the Fed eases its policy, mortgage rates are likely to continue moving downwards, alleviating some of the housing affordability issues that many consumers are experiencing.
What are the expected effects of the Federal Reserve rate cut on economic growth?
The recent Federal Reserve rate cut is expected to promote economic growth. By reducing borrowing costs, it will encourage consumer spending and investment, potentially leading to job creation and slightly increased inflation over the next six to twelve months.
When can consumers expect to see the benefits of the Federal Reserve rate cut in their loans?
Consumers may experience relief in loan payments, such as credit cards and car loans, due to the recent Federal Reserve rate cut. However, interest rates are also influenced by market expectations and repayment risks, and substantial changes may take several months to materialize.
What does the Federal Reserve rate cut mean for inflation levels?
A Federal Reserve rate cut can lead to slightly higher inflation rates in the future. The decision to lower interest rates is aimed at stimulating economic growth and could cause inflation to tick up as demand increases.
How might the Federal Reserve rate cut affect consumer credit?
The Federal Reserve rate cut is likely to encourage banks to lower credit card interest rates and offer better loan terms. While consumers may see some relief in borrowing costs due to this policy, prevailing market conditions will also play a significant role in determining actual rates.
Is it likely that the Federal Reserve will implement more rate cuts in the near future?
Yes, the Federal Reserve signaled the potential for additional rate cuts later this year. Economists anticipate that the Fed may implement two more rate cuts if economic indicators, particularly job growth and inflation, signal a need for further action.
What is the connection between the Federal Reserve rate cut and consumer spending?
The Federal Reserve rate cut helps lower borrowing costs, making it cheaper for consumers to take out loans. This encourages spending on big-ticket items, such as homes and cars, thus boosting overall economic activity.
What should homeowners consider with the recent Federal Reserve rate cut?
Homeowners and prospective buyers should consider refinancing their mortgages or taking out new loans, as the Federal Reserve rate cut is likely to drive mortgage rates lower, making home loans more affordable.
How does a Federal Reserve rate cut influence financial markets?
A Federal Reserve rate cut usually leads to increased investor confidence in financial markets. Lower interest rates make borrowing cheaper, which can stimulate business investment, leading to rising stock prices and improved market conditions.
Why does the Federal Reserve cut rates during periods of economic uncertainty?
The Federal Reserve cuts rates during economic uncertainty to stimulate growth and prevent recession. Lower interest rates make borrowing easier for consumers and businesses, supporting spending and investment to help stabilize the economy.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| First Rate Cut in Four Years | The Federal Reserve cut the key interest rate by 0.5 percentage points, its first reduction in four years. |
| Impact on Borrowing Costs | Borrowing costs for credit cards, car loans, and mortgages are expected to decrease, making loans more affordable for consumers. |
| Future Cuts Anticipated | The Fed signals that more rate cuts may follow, potentially totaling two additional cuts by the end of the year. |
| Fed’s Strategy and Market Response | The Fed intends to recalibrate its policy based on economic indicators such as inflation and unemployment. |
| Housing Market Effects | Mortgage rates expected to decline further, but affordability remains a challenge in the housing market. |
| Consumer Relief Timeline | Consumers may experience delayed relief as interest rates will remain relatively high for the next several months. |
Summary
The recent Federal Reserve rate cut marks a significant move in the U.S. economy, with the aim of reducing borrowing costs for consumers. As the Fed reduces rates, it is expected to provide relief to those with credit card debt, car loans, and potential homebuyers. While the rate cut is a positive signal, the timeline for broader economic benefits remains uncertain, with factors such as inflation and labor market performance influencing future decisions. The Fed’s proactive strategy suggests that if the economy shows signs of deterioration, further rate cuts may follow, supporting continued job creation and economic growth in the evolving landscape.