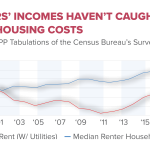
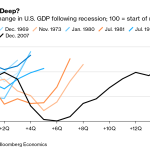
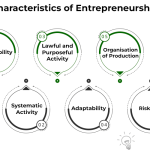
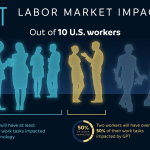
Entrepreneurialism is reshaping the landscape of work, transforming how individuals engage with their careers and the economy. As more people venture into self-employment, this movement is not only fostering innovation but also driving job creation across various sectors. From solopreneurs who carve out niche markets to the rise of the freelance economy, those embracing entrepreneurialism are becoming the backbone of the modern workforce. This shift reflects a broader trend where traditional job roles are being supplemented—or even replaced—by individuals taking charge of their professional destinies. With an increasing emphasis on business innovation, understanding the essence of entrepreneurialism is essential for navigating today’s dynamic economic environment.
In today’s fast-paced economy, the concept of entrepreneurship has gained heightened visibility, often synonymous with self-started ventures and innovative business practices. This phenomenon encompasses a wide array of activities, from freelancers hustling to build their own brands to individuals exploring alternative career paths as solopreneurs. The freelance economy is thriving, offering new avenues for job creation that disrupt traditional employment models. Many are drawn to this shift not only for its financial prospects but also for the promise of autonomy and fulfillment in their work. As society continues to evolve, the drive for entrepreneurial pursuits becomes increasingly relevant, challenging conventional notions of success and job satisfaction.
The Evolution of American Entrepreneurialism
American entrepreneurialism has undergone a significant transformation, rooting itself in the American Dream, where individuals believe they can create their own paths. This evolution traces back to the late 19th century, when industrialization began to reshape the job landscape. As factories automated and the demand for traditional labor diminished, people sought new avenues for employment. This shift has been characterized by an increasing number of individuals identifying as entrepreneurs, freelancers, and solopreneurs. Just as Erik Baker illustrates in “Make Your Own Job,” the very definition of entrepreneurialism expanded during pivotal economic moments, revealing a cultural shift towards personal initiative and leadership.
The late 20th century intensified this trend, as job security became a relic of the past. With the rise of the internet and technology, the freelance economy flourished, allowing individuals to carve niches for themselves. Entrepreneurialism became synonymous with freedom and self-reliance. Writers like Napoleon Hill called for a mindset focused on leveraging one’s unique skills and knowledge to create opportunities, reflecting how American entrepreneurialism emphasizes innovative thinking that transcends traditional definitions of work. Today, the spirit of entrepreneurialism remains strong in American society, fueling aspirations across various sectors.
The Freelance Economy and Its Impact
The freelance economy has reshaped the ways individuals engage with work, marking a departure from conventional jobs towards more flexible arrangements. In this new landscape, freelancers have emerged as critical players, contributing significantly to job creation and economic growth. Thanks to advancements in technology, individuals can offer their services globally, whether as graphic designers, content creators, or consultants. This thriving market is a testament to the changing dynamics of employment, where job titles are less rigid, and the focus is on skills and deliverables rather than hierarchical positions.
However, the rise of the freelance economy is not without its challenges. As Baker discusses, this freedom can come with an underlying anxiety, as many freelancers face uncertainties about income and job stability. The sense of ownership in one’s career can lead to a constant hustle, where individuals are perpetually seeking new clients and projects. This paradigm shift necessitates that freelancers adapt and innovate continuously, making the entrepreneurial mindset essential for success. In navigating this landscape, aspiring freelancers must also embrace the principles of self-promotion and resilience that underpin American entrepreneurialism.
Solopreneurs: The Rise of Individual Entrepreneurs
Solopreneurs are individuals who embark on their entrepreneurial journeys independently, leveraging their skills and passions to create sustainable businesses. This burgeoning group has played a significant role in shaping the landscape of American entrepreneurialism. In recent years, more professionals have opted to venture into solopreneurship, opting for autonomy over traditional employment pathways. They embrace their expertise and market themselves, often navigating multiple roles as both the creator and marketer of their products and services.
The rise of solopreneurs is fueled by a desire for greater work-life balance and fulfillment, aligning closely with the ethos of the freelance economy. As Baker notes, this movement contrasts sharply with previous generations who might have viewed job stability as the pinnacle of success. Instead, solopreneurs redefine success through flexibility, creativity, and personal satisfaction. Yet, they also face the ongoing pressure to innovate continually, reflecting the relentless ambition synonymous with entrepreneurialism. The challenges and triumphs of solopreneurs showcase the evolving nature of work in America.
Job Creation Through Entrepreneurial Innovation
Entrepreneurial innovation serves as a powerful catalyst for job creation across various industries. Startups and small businesses are often at the forefront of economic development, driving technological advancements and utilizing creative approaches to meet consumer demands. Baker emphasizes this notion in his analysis, suggesting that entrepreneurialism is not merely about individual gains but about contributing to the broader economic ecosystem. By establishing new enterprises, entrepreneurs and freelancers alike help sustain employment and spark growth in their communities.
This connection between innovation and job creation invites a deeper analysis of the factors that foster a thriving entrepreneurial environment. For example, supportive policies, access to funding, and mentorship can enhance an entrepreneur’s ability to translate ideas into viable products or services. In an era where traditional employment is being redefined, fostering a culture of entrepreneurship can yield significant benefits for society at large, highlighting the importance of nurturing talent and innovation among aspiring entrepreneurs.
The Psychological Aspect of Entrepreneurialism
Entrepreneurialism is not just about economic outcomes but also has profound psychological implications for individuals navigating this path. The pressure to succeed and the fear of failure can lead to heightened anxiety, as chronicled by Baker’s examination of American work culture. Many entrepreneurs and freelancers experience a constant state of hustle, where the boundaries between personal and professional life blur. This psychological burden underscores the reality that entrepreneurialism requires a unique mindset, often resulting in both exhilaration and exhaustion.
Moreover, the quest for entrepreneurship can lead to self-discovery and personal growth, as individuals learn to harness their skills and overcome challenges. The entrepreneurial journey often prompts reflection on one’s values, goals, and definitions of success. As Baker illustrates, this balance between ambition and well-being is vital for sustaining a thriving entrepreneurial spirit. Encouraging a healthy approach to entrepreneurialism, where mindfulness and self-care are prioritized, can foster resilience and encourage long-term success.
Technological Advancements and Their Influence on Jobs
Technological advancements have drastically altered the landscape of work and entrepreneurship, creating both opportunities and challenges for job seekers. In the past few decades, technology has automated numerous tasks, leading to the decline of some traditional roles while simultaneously giving rise to new industries and professions. As highlighted by Baker, this evolution forces individuals to adapt or risk becoming obsolete, driving many toward entrepreneurship as they seek to redefine their careers.
For those who embrace innovation, the technological revolution offers unprecedented tools to launch and scale businesses. From social media marketing to e-commerce platforms, entrepreneurs now possess powerful resources to reach global markets. However, the rapid pace of change also demands continuous learning and adaptation, where individuals must refine their skills to remain competitive. Navigating this dynamic environment illustrates the importance of fostering a culture of lifelong learning to support sustainable entrepreneurialism.
Navigating the Challenges of the Gig Economy
The gig economy, closely tied to the rise of freelance work and entrepreneurship, presents unique challenges for workers and entrepreneurs alike. While it offers flexible working conditions and the allure of independence, gig workers often find themselves battling inconsistent income and a lack of benefits that traditional employees enjoy. Baker’s insights on the realities of working in a gig economy serve as a reminder that while entrepreneurialism can be empowering, it also comes with significant risk.
To thrive in the gig economy, individuals must adopt a growth mindset, continuously adapting their skills and approaches to meet market demands. Organizations and policymakers can play a crucial role by developing frameworks that support gig workers, ensuring they have access to resources, training, and financial services. Addressing the inherent instability of gig work is vital to creating a sustainable environment where entrepreneurialism can flourish without compromising personal welfare.
The Future of Work: Embracing Entrepreneurial Spirit
As we move into an unpredictable future, embracing the entrepreneurial spirit becomes essential for navigating the evolving landscape of work. Changes in technology, market demands, and societal values will continue to reshape how we define work and success. Baker’s exploration of American entrepreneurialism encourages readers to consider how future professionals can cultivate their entrepreneurial skills and mindsets, preparing them for varied career paths that may not adhere to traditional structures.
Moreover, fostering an entrepreneurial spirit will require collaboration and innovation at all levels—from individuals to organizations to educational institutions. By creating ecosystems that prioritize creativity and entrepreneurship, we can better equip future generations to tackle emerging challenges and seize opportunities in an increasingly complex job market. Embracing entrepreneurialism not only benefits individuals but also cultivates resilient economies capable of withstanding change.
Understanding the Cultural Shift in Work Ethic
The cultural shift towards entrepreneurialism reflects changing notions of work ethic in American society. No longer is hard work solely defined by long hours or traditional employment; instead, it encompasses creativity, adaptability, and a proactive approach to career development. As Baker highlights in his work, individuals are encouraged to align their careers with their passions and skills, effectively redefining what it means to work hard.
This shift mirrors larger societal changes, including the pursuit of personal fulfillment and the need for work-life balance. The emphasis on pursuing one’s own entrepreneurial path is a testament to the evolving understanding of career success. Encouraging young professionals to engage with their ambitions supports a culture that values individual contributions while emphasizing the importance of collaboration and innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does American entrepreneurialism play in job creation?
American entrepreneurialism significantly influences job creation by encouraging innovation and the establishment of new businesses. Entrepreneurs fill gaps in the economy by developing products and services that meet emerging needs, thus leading to the creation of jobs. This cycle of job creation contributes to a more dynamic and adaptable labor market.
How does the freelance economy exemplify modern entrepreneurialism?
The freelance economy exemplifies modern entrepreneurialism by allowing individuals to leverage their skills and expertise to create their own job opportunities. With platforms for freelancers growing in popularity, many solopreneurs and independent contractors thrive, showcasing the flexibility and innovation that defines today’s entrepreneurial landscape.
What is the significance of solopreneurship in the context of entrepreneurialism?
Solopreneurship is significant in the context of entrepreneurialism as it represents a shift towards individualism and self-directed work, offering professionals the freedom to build businesses based solely on their skills and interests. This trend reflects a broader societal change where traditional employment paths are no longer seen as the only option for successful careers.
How does business innovation relate to the rise of entrepreneurialism?
Business innovation is a core aspect of entrepreneurialism, driving the development of new ideas and practices that reshape industries. Entrepreneurs thrive on innovation, using it to solve problems and create value, which not only enhances their own businesses but also inspires broader economic growth and competitiveness.
Why is understanding American entrepreneurialism important for aspiring entrepreneurs?
Understanding American entrepreneurialism is crucial for aspiring entrepreneurs because it provides insights into the historical context and evolving practices that shape the business landscape. By studying past shifts in work culture and the impact of entrepreneurial thought, individuals can better navigate their own entrepreneurial journeys and contribute effectively to the economy.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Rise of Entrepreneurialism | The book ‘Make Your Own Job’ discusses how entrepreneurialism has transformed people’s view of work in America. |
| Diverse Forms of Entrepreneurs | Includes founders, managers, ride-share drivers, influencers, solopreneurs, etc. |
| Historical Context | America’s shift towards entrepreneurialism began in the late 19th century due to declining factory jobs. |
| Cultural Shift | The focus changed from a strong work ethic to one encouraging personal skills and ambition. |
| Influence of Self-help Literature | Books like ‘Think and Grow Rich’ emphasized entrepreneurship and self-promotion. |
| Post-War Enthusiasm | Entrepreneurialism gained traction in various fields beyond economics during the mid-20th century. |
| Current Trends | Today, the concept of entrepreneurialism continues to thrive, driven by fears of job displacement. |
| Psychological Impact | The constant pressure to be entrepreneurial can lead to anxiety and a lack of relaxation. |
Summary
Entrepreneurialism is reshaping the landscape of work and how we perceive our careers. As outlined in Erik Baker’s ‘Make Your Own Job’, this shift reflects a historical transition from traditional employment towards a self-guided, dynamic approach. The rise of various forms of entrepreneurs highlights the necessity for individuals to adapt and thrive amid the uncertain nature of the modern economy. The implications of this change are profound, as they affect not only our job structures but also our mental and emotional well-being, illustrating the complexities inherent in this entrepreneurial culture.