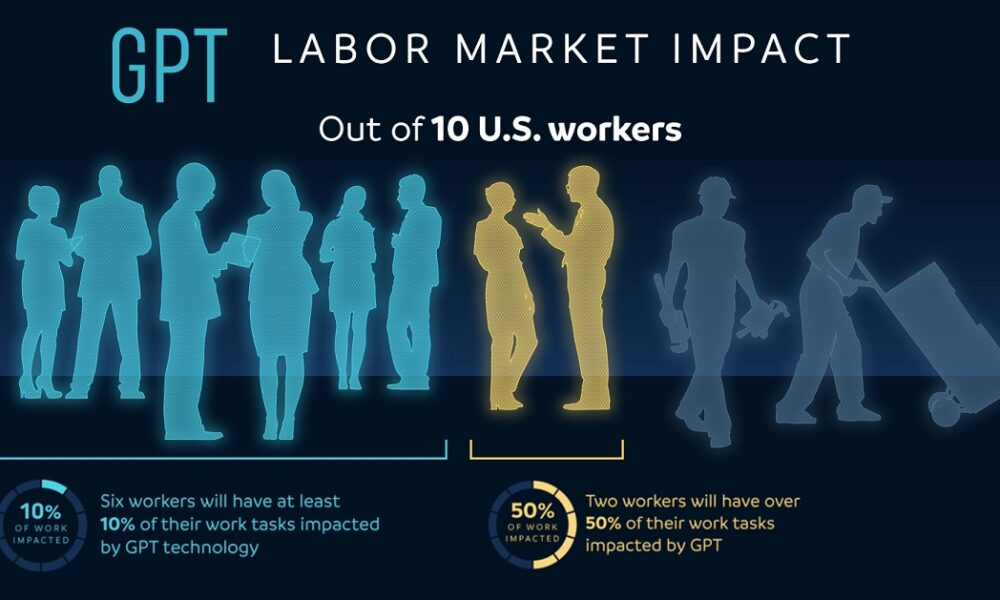
The impact of AI on the labor market is already becoming a central topic in discussions about the future of work. A recent study by Harvard economists highlights how artificial intelligence is not just a fleeting trend but a significant force reshaping labor market dynamics. With evidence showing a shift in occupational churn, researchers are tracking how technology and jobs are evolving together amid increasing automation. This transformation points to notable labor market trends that hint at a reallocation of jobs, particularly in the STEM fields, while low-wage service roles face decline. As we delve into this phenomenon, understanding AI’s labor market impact becomes essential for employees and employers alike, adapting to the changes it brings.
Exploring the ramifications of intelligent systems on employment reveals a broader narrative about work in the 21st century. The emergence of smart technologies is influencing job structures, prompting discussions around employment viability and skill requirements. As labor sectors undergo significant shifts, it’s essential to examine how these innovations, characterized by occupational evolution and market volatility, reshape traditional professions. The dynamic interplay between automation and opportunity reflects the changing landscape of the workforce, indicating that professionals across all fields must adapt to maintain their relevance and competitive edge. In this unfolding scenario, understanding the intersection of technology and job evolution is more crucial than ever.
The Rise of AI in the Workforce
The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) represents a seismic shift in the workforce, altering how businesses operate and how employees engage with their tasks. Historical analysis indicates that the current wave of AI could be compared to monumental technological milestones like the introduction of electricity and the computer. As highlighted in the study by economists David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers, AI is now a core driver of change in labor market dynamics, leading to increased efficiency but also raising concerns about job displacement.
As sectors pivot towards advanced AI solutions, professionals across various fields are observing a disruption in traditional job roles. The rise of AI has led to increased demand for skilled professionals in STEM fields, as organizations seek talent that can harness the power of technology. With AI steering labor market trends, many individuals must upskill to meet the evolving demands of their professions, ensuring they remain relevant in an increasingly automated workplace.
Changing Labor Market Trends
Labor market trends have historically reflected broader economic shifts, but the current transformation driven by AI poses unique challenges and opportunities. The study’s insights on occupational churn reveal that while innovation can lead to job creation, it also incites volatility, especially in sectors like retail and low-paid services. Over the past decade, a marked decline in traditional roles has emerged, signaling a potential future where technology drastically reshapes job availability and security.
Researchers note an observable pattern of job polarization, particularly as automation increases efficiencies at the upper end of the skill spectrum. This shift emphasizes the growing need for highly trained workers, effectively sidelining low-skilled positions. As the labor market continues to adapt to these changes, understanding the interplay of technology and jobs becomes critical for policymakers and workforce development agencies aiming to mitigate the impacts of AI on employment.
Occupational Churn and Its Implications
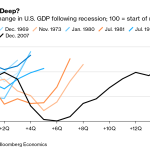
Occupational churn refers to the continual movement and turnover of jobs within the labor market. David Deming’s research indicates that while there have been periods of stability, the recent trends tied to AI suggest a new era of turbulence. From 2019 onwards, the data suggests that the pace of occupational change has accelerated, reflecting both the rapid adoption of AI and shifts in consumer behavior, influenced partly by the pandemic.
The implications of this churn are vast. As certain occupations decline, particularly in low-wage industries, workers may face significant hurdles in retraining for new roles in more technologically advanced fields. The study underscores that understanding these dynamics is essential for both employers and job seekers, as the landscape of the labor market continues to evolve rapidly in the wake of technological progression.
The Future of Work in an AI-Driven World
The evolving landscape of the labor market brings to the forefront the concept of the future of work, particularly within the realm of AI. With AI tools now embedded in various industries, the workplace of tomorrow is set to prioritize technology-driven roles and skills. This transformation necessitates strategic planning from educational institutions and employers to prepare the workforce adequately to thrive in this new environment.
Additionally, the future of work raises questions about job satisfaction and the nature of work-life balance in an increasingly automated setting. As AI tools take over routine tasks, workers might find themselves focusing more on complex problem-solving and creativity, potentially leading to enhanced job fulfillment. However, this shift also places pressure on individuals to continually adapt and learn new skills to remain competitive in the job market.
Understanding the Impact of AI on Employment
The impact of artificial intelligence on employment is a central theme in today’s discussions on labor market trends. With the advent of AI technologies, many jobs face the threat of automation, leading researchers to predict shifts in employment distribution across various sectors. The findings from the Harvard study highlight this duality—while AI could create new opportunities, it also harbors the potential for substantial job losses, particularly in low-skilled roles.
To mitigate these impacts, ongoing education and training become crucial. Employers must invest in their workforce, ensuring that their employees can adapt to the technological advancements that AI introduces. Simultaneously, understanding these changes can equip workers with the knowledge necessary to navigate their careers effectively in an AI-enhanced labor market.
STEM Jobs on the Rise due to AI
A notable trend arising from AI’s implementation is the significant growth in STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) jobs. According to the research by Deming and Summers, the share of STEM positions has surged, reflecting a nearly 50% increase from 2010 to 2024. This growth emphasizes a crucial shift in the labor market towards roles that require high levels of specialized training and technical expertise.
The increased demand for STEM talent not only highlights the importance of education focused on these fields but also suggests a long-term societal shift towards a more technology-driven economy. Businesses are actively seeking employees who can navigate complex technological systems, pointing to a future where the backbone of many industries could rest heavily on crushing views of automation and AI.
The Decline of Low-Paid Service Jobs Post-AI
The analysis of labor trends reveals a troubling decline in low-paid service jobs, a pattern somewhat accelerated by the introduction of AI into business operations. As automated systems handle more routine tasks, roles traditionally filled by human workers, especially in service sectors, have seen a decrease. This decline points to a worrying future for employees in these positions, especially given that many of these roles may not return to pre-2019 levels.
This unsettling trend underscores the importance for workers in such sectors to seek alternate career paths or to reskill for more stable employment opportunities. As industries shift towards automation, being proactive in acquiring new skills is not only advantageous but critical for personal job security.
Navigating Automation Anxiety in the Workforce
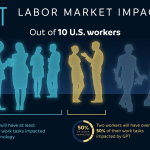
The rise of AI has incited feelings of anxiety regarding automation among the workforce—a phenomenon termed ‘automation anxiety.’ Many workers fear that the growing implementation of AI technologies will threaten their job security and livelihood. Indeed, the predictions that significant percentages of jobs are at risk resonate deeply, highlighting the urgent need for proactive measures to address these concerns.
In this context, employers and industry leaders must work collaboratively with employees to develop clear communication strategies about the integration of AI. This can help assuage fears by focusing on the opportunities AI presents, such as enhancing productivity and creating new job roles. By fostering an open dialogue around automation, the workforce can shift from anxiety to adaptability.
The Role of Policymakers in AI Disruption
As the labor market undergoes profound changes due to AI, the role of policymakers becomes increasingly vital in shaping a responsive framework. Effective policies can address the displacement of workers and the need for retraining programs, ensuring that the workforce can adapt to new demands. There is an urgent requirement for governments to collaborate with educational institutions and businesses, implementing initiatives that prepare individuals for the jobs of the future.
Moreover, policymakers must address potential inequities resulting from these rapid changes. Strategies aimed at promoting inclusive growth can help mitigate the adverse effects of displacement and ensure that all workers, regardless of their backgrounds, have access to opportunities in an AI-driven economy. Crafting a comprehensive approach to technology and jobs will be essential for a resilient workforce.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of AI on labor market trends?
The impact of AI on labor market trends is significant, leading to changes in job distribution. Recent studies show that AI is promoting well-compensated roles requiring high levels of training, while low-paid service jobs are declining. As AI technologies evolve, they reshape not only job demands but also the skills necessary for future employment.
How does artificial intelligence influence occupational churn in the labor market?
Artificial intelligence influences occupational churn by accelerating the pace at which jobs are created and displaced. A recent study measuring over a century of data indicates that while there was stability between 1990 and 2017, AI is now driving more rapid changes in the workforce, resulting in fluctuations in job categories and skill requirements.
Are automation and AI responsible for job loss in the workforce?
Yes, automation and AI are contributing to job loss in specific sectors, particularly low-paid service jobs. The decline in these positions began around 2019, suggesting that while AI improves productivity, it also displaces certain roles, adding to concerns about the future of work for low-skill job markets.
What trends can we expect in the future of work due to AI advancements?
The future of work due to AI advancements suggests a rise in STEM job opportunities, as well as a polarization in wage distributions. Industries are increasingly investing in advanced technologies, leading to a greater demand for tech-savvy professionals while potentially decreasing opportunities for lower-paid service roles.
How is e-commerce affected by artificial intelligence in the labor market?
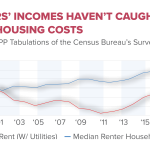
E-commerce has experienced significant growth due to artificial intelligence, particularly in predictive analytics. Since 2015, the share of retail sales in e-commerce has doubled, impacting the labor market by reducing the number of retail sales jobs as consumer behavior shifts toward online shopping.
What does ‘automation anxiety’ refer to in the context of the labor market?
Automation anxiety refers to the widespread concern about job displacement due to increasing automation and AI capabilities. This phenomenon gained attention in the early 2000s, with predictions that a large percentage of U.S. jobs could be at risk from technological innovations, highlighting the need for workers to adapt to new skill sets.
How has AI changed the composition of jobs in the United States?
AI has notably changed the composition of jobs in the U.S. by increasing the demand for high-skilled positions, particularly in technology and STEM fields. As traditional roles decline, firms are pursuing a more educated workforce, resulting in significant shifts in job distribution and required competencies.
What role does investment in AI play in labor market volatility?
Investment in AI plays a crucial role in labor market volatility by driving innovation and creating new job opportunities while simultaneously displacing certain job categories. As companies adopt AI technologies, the demand for skilled workers rises, reshaping the overall employment landscape and contributing to changes in labor market trends.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| AI Disruption | A study shows AI is causing significant changes in the U.S. labor market, indicating a new period of occupational churn. |
| Historical Context | For decades, the job market was stable; however, volatility increased from 2019 onward. |
| Job Polarization | The traditional trend of job polarization is shifting towards higher-wage jobs requiring more training. |
| Growth in STEM Jobs | STEM jobs have increased notably from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024. |
| Decline in Service Jobs | Specifically low-paid service jobs are declining; many may not return post-pandemic, |
| Retail Job Losses | Retail sales jobs have decreased by 25% from 2013 to 2023 due to technological advancements. |
Summary
The AI labor market impact is becoming increasingly apparent as new research indicates significant shifts in occupational trends. While stability marked the labor force from 1990 to 2017, evidence shows a recent surge in AI influence since 2019, leading to volatility in job markets and the rise of higher-wage positions requiring advanced skills. As industries adapt to integrate AI technologies, low-paid service and retail jobs are declining sharply, suggesting that barriers to previous levels of employment may likely be permanent. The study emphasizes the need for professionals across all sectors to understand and adapt to these changes, as AI continues to transform the fabric of the workforce.